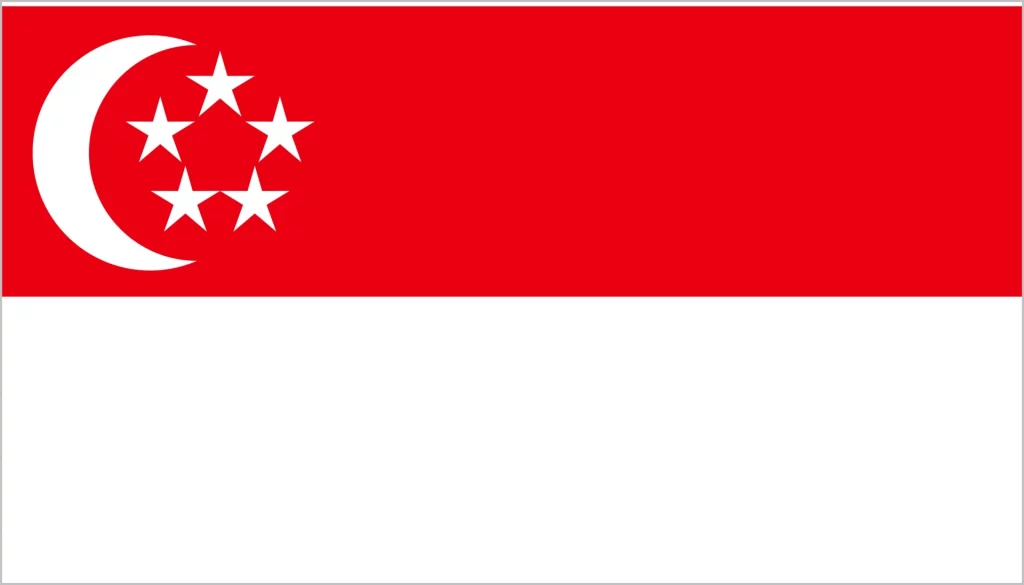
Singapore is a small island city-state located off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula in Southeast Asia. Despite its diminutive size of just 719 square kilometers, Singapore punches well above its weight on the global stage thanks to its strategic location, pro-business policies, and visionary leadership. Here is an in-depth look at this remarkable country. Let’s explore the fascinating things in Singapore together with TripWordwide.
A brief introduction about Singapore
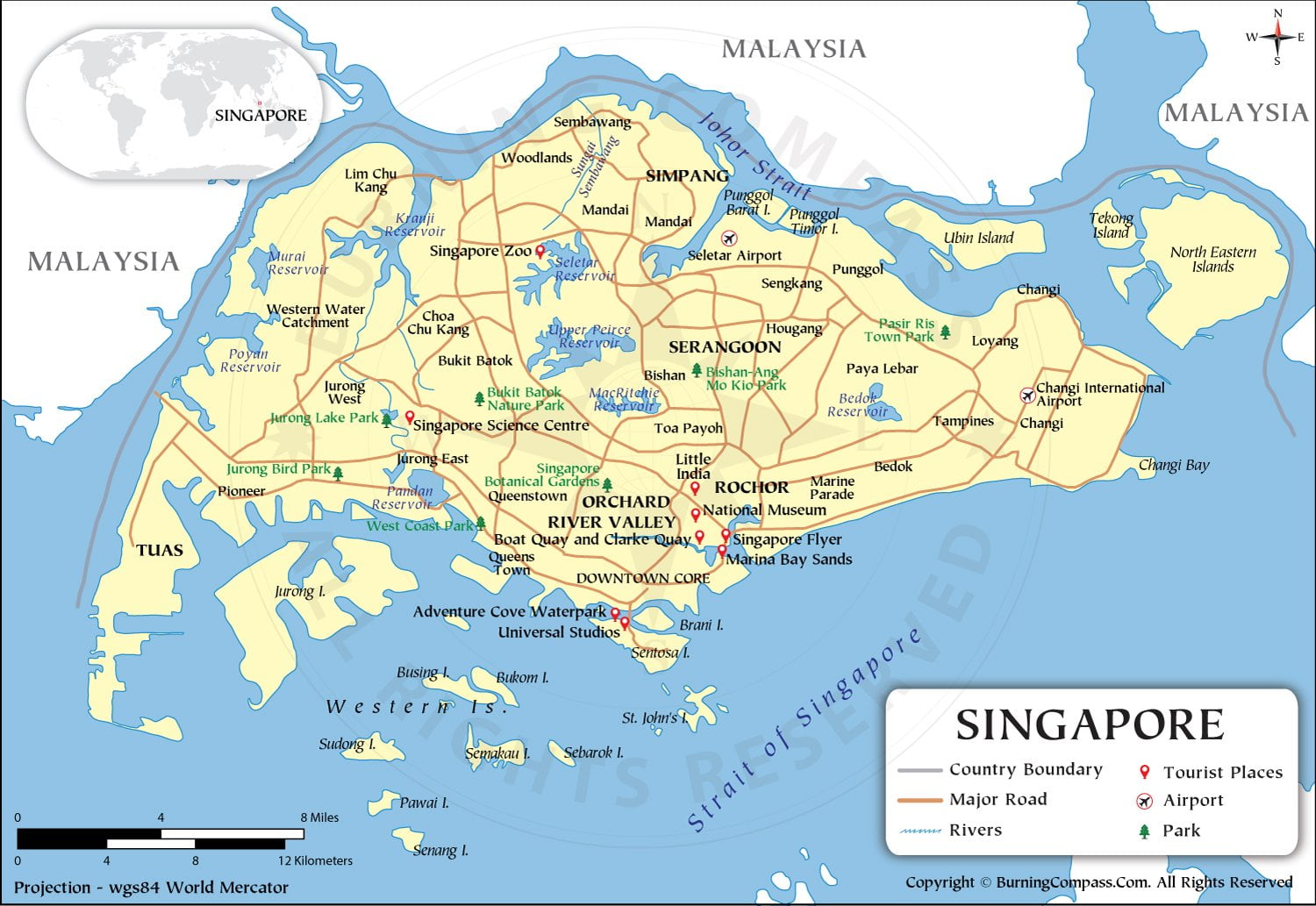
Singapore is an island country made up of one main island and over 60 smaller islets. With a total land area of 722 square kilometers, it is one of the smallest countries in the world, which earned it the nickname “Little Red Dot with Big Ambitions“.
Singapore lies 137 kilometers north of the equator and just south of Peninsular Malaysia. It is situated at the southern entrance to the Straits of Malacca, which connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean. This strategic location has allowed Singapore to become a bustling center of trade and finance.
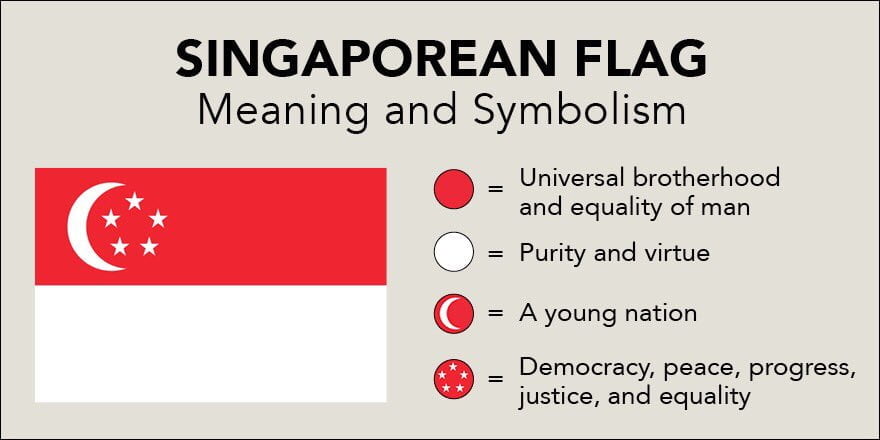
Singapore has a population of around 5.7 million as of 2023. It is a highly urbanized and densely populated country, with most residents living in public housing built by the government.
There are four official languages – English, Malay, Mandarin Chinese, and Tamil. Singapore has a highly diverse, multicultural population comprising of Chinese, Malay, Indian, and Eurasian ethnicities.
Weather forecast Singapore
Singapore typically experiences a tropical rainforest climate, with high humidity and consistent temperatures throughout the year. According to the latest weather forecast, the upcoming week will see partly cloudy skies with occasional showers, especially during the afternoon and evening due to the monsoon influence.
Daily temperatures are expected to range between 26°C to 32°C. Thunderstorms may occur on some days, so residents and visitors are advised to carry an umbrella and check updates from the Meteorological Service Singapore regularly.
Best time to visit Singapore
The best time to visit Singapore is generally between February and April, when the weather is relatively dry and outdoor activities are most enjoyable.
This period falls between the two major monsoon seasons, offering visitors more sunshine and less rainfall. For travelers seeking the ideal time to travel to Singapore, these months provide the most pleasant climate for sightseeing, shopping, and exploring cultural festivals.
While Singapore is a year-round destination due to its tropical climate, the peak travel season often coincides with major holidays and events such as Chinese New Year and the Singapore Grand Prix.
On the other hand, the off-peak months like July and August can be more affordable, although they come with higher humidity and occasional heavy showers.
Whether you’re planning a family holiday, a romantic getaway, or a solo adventure, understanding the Singapore travel season helps ensure a smooth and memorable trip.
Did Singapore Airlines Have a Concorde?
Yes, Singapore Airlines did operate a Concorde, but not in the traditional sense. In the late 1970s, Singapore Airlines formed a unique partnership with British Airways to co-operate a supersonic Concorde jet on the London–Bahrain–Singapore route.
The aircraft, a British Airways Concorde, featured dual branding, with Singapore Airlines livery on one side and British Airways on the other.
This joint Concorde service marked one of the rare instances where a supersonic aircraft carried the branding of two international airlines.
The Singapore Airlines Concorde route began in 1977 but was discontinued shortly after due to airspace restrictions over Malaysia and high operational costs.
Although short-lived, this collaboration remains a notable chapter in the history of supersonic travel, highlighting Singapore Airlines’ ambition to offer cutting-edge experiences. Today, the Concorde is remembered as an aviation icon, and its brief association with Singapore Airlines continues to fascinate aviation enthusiasts.
Postal Codes and Time Zone of Singapore
Singapore uses a six-digit postal code starting with the number 6. The first two digits represent the postal sector, the next two digits represent the postal district, and the last two digits represent the building number. For example, the postal code for Marina Bay Sands is 018971.
Singapore is 8 hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT+8). It does not observe daylight saving time.
Geography and Climate of Singapore
Singapore consists of one main island surrounded by over 60 smaller islets. The main island is highly urbanized, with a hilly interior and coastlines marked by estuaries and sandy beaches. About 23% of Singapore’s total land area comprises of forest and nature reserves, with tropical rainforests covering the center of the main island.
Located near the equator, Singapore has a tropical climate with abundant rainfall, high humidity, and uniform temperatures throughout the year. Daily temperatures range from 24°C to 31°C. There are no distinctive seasons, although November to January are the wettest months.
History and Independence of Singapore
Modern Singapore was founded in 1819 by Sir Stamford Raffles as a trading post of the British East India Company. It grew into an important seaport and became the capital of the Straits Settlements in 1832. During World War II, Singapore was occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1945.
After the war, Singapore joined the Federation of Malaya in 1963. However, it separated and became fully independent in 1965 due to political and economic differences. Singapore’s first prime minister was Lee Kuan Yew, who led the country from 1959 to 1990. Under his leadership, Singapore rapidly transformed from a British colonial outpost into a prosperous nation.
Government and Politics
Singapore is a parliamentary representative democratic republic with a Westminster system of unicameral parliamentary government. The head of state is the President, who is elected by popular vote. The Prime Minister is the head of government and is appointed by the President from Members of Parliament.
The ruling party since independence has been the People’s Action Party (PAP). Singapore has a highly centralized government with the PAP dominating the political scene. There are tight restrictions on free speech and assembly. However, Singapore does have general elections regularly. The last one was in 2020 where the PAP retained its supermajority.
While not fully democratic by Western standards, the PAP’s authoritarian form of government has provided economic stability and growth for Singapore. The country consistently ranks high on indicators of good governance.
Economy Singapore 2025
Singapore has a highly developed free market economy that depends heavily on trade and manufacturing. Although lacking natural resources, Singapore exploits its strategic location and skilled workforce to attract investment and serve as Southeast Asia’s financial and high-tech hub.

Key sectors include electronics, chemicals, financial services, oil drilling equipment, petroleum refining, rubber processing, and processed food and beverages. Singapore is also a popular tourist destination, receiving over 19 million visitors in 2019.
Singapore ranks 2nd on the ease of doing business index and has one of the world’s highest per capita GDPs at over US$85,000 as of 2022. Its main trading partners are China, Malaysia, Indonesia and the United States.
Population and Demographics
As of 2023, Singapore has an estimated population of 5.7 million people. The median age is 42 years old. About 74% of the population are Chinese, 13.5% are Malay, 9% are Indian and 3.2% are of other descent. The main religions are Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, Taoism and Hinduism.
The population density is an incredible 8,358 per square kilometer, making it the 3rd most densely populated country globally. This is attributed to Singapore’s limited land area and extensive use of land reclamation over the decades to expand the island.
To tackle its aging population and shrinking workforce, Singapore has been trying to increase its fertility rate and encourage immigration. The current fertility rate is around 1.14 births per woman, one of the lowest in the world.
Culture and Society
Singapore is a multicultural society with a diverse mix of ethnic groups and immigrants. English is the language of administration and business while Malay, Mandarin and Tamil are official languages. Most Singaporeans are bilingual.
Despite rapid economic development, Singapore has preserved many aspects of its Asian heritage and cultural practices. Fusion cuisine combines Chinese, Malay and Indian influences. Public holidays reflect its multi-ethnic population.
Singaporean culture emphasizes Asian values such as strong families, education, discipline and hierarchy. Society is more collective than individualistic. The government actively promotes racial and religious harmony as ethnic rifts could destabilize the small country.
Challenges Ahead
As a small, resource-scarce country, Singapore faces considerable challenges moving forward:
- Declining birth rates and aging population threaten its workforce size and economic dynamism.
- Rising costs of living and widening income inequality risk diminishing quality of life.
- Heavy dependence on foreign investment and exports makes it vulnerable to global downturns.
- Land constraints limit options for future expansion.
- Water scarcity necessitates reliance on imported water from Malaysia.
To address these challenges, Singapore will need to continue leveraging technology and innovation to improve productivity, restructure its economy, and stay nimble amidst shifting global conditions. Its future remain bright if it can stay open and pragmatic.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the postal code for Singapore?
A: Singapore postal codes are 6 digits starting with 6, e.g. 018971 for Marina Bay Sands. The first 2 digits represent the postal sector, the next 2 represent the postal district, and the last 2 represent the specific building.
Q: What time zone is Singapore located in?
A: Singapore is 8 hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT+8). It does not observe daylight saving time.
Q: Is Singapore part of Malaysia?
A: No, Singapore is an independent country. It was briefly part of Malaysia from 1963 to 1965 before becoming fully sovereign.
Q: Why did Singapore separate from Malaysia?
A: There were disagreements over governance and economic policies. Singapore also faced racial tensions as the Chinese-majority PAP government clashed with federal Malaysian leaders. Separation was deemed the best path forward.
Q: How long was Singapore a British colony?
A: Singapore was under British colonial rule from 1819 when Sir Stamford Raffles founded a trading settlement, until 1963 when it joined the Federation of Malaya.
Q: What is the population of Singapore in 2023?
A: Singapore has an estimated population of 5.7 million people as of 2023. It is the 3rd most densely populated country in the world.
In summary, Singapore is a remarkable country. Despite having little land and resources, through strategic location, stable governance, and future-oriented policies, Singapore has transformed into a global hub for business, finance, and technology.
However, it faces demographic and economic challenges moving ahead. Singapore must continue adapting quickly and creatively to maintain its competitive edge. Its efficient governance and educated workforce provide strong fundamentals for success. By upholding openness, pragmatism and multicultural harmony, Singapore can continue thriving well into the future.

